Understanding seasonal search trends
Seasonal search trends are a crucial factor influencing the performance of your online content. These trends, which vary according to season and time of year, play a key role in how users interact with online content. They can affect everything from the number of visits to your site to the performance of your online advertising campaigns.
Impact of seasonal search trends on your content
Seasonal search trends can have a major impact on the success of your online content. For example, during the festive season, searches related to gifts and online shopping increase dramatically. So if you run an e-commerce site, it's crucial to optimise your content around these trends to attract more traffic and increase your sales.
Adapt your content to seasonal search trends
Adapting your content to seasonal search trends is not only a great strategy for improving your online performance, it's also a necessity in today's competitive digital environment. By being aware of these trends and adjusting your content accordingly, you can ensure that your message reaches your target audience when it is most relevant and most likely to prompt action.
Measuring the impact of seasonal search trends
Measuring the impact of seasonal search trends on your content is an essential step in understanding the effectiveness of your content strategy. This can be done by tracking your site traffic, conversion rates and other key performance indicators that can tell you how your content is performing according to seasonal variations in search trends.
Need a website?
Ask for a free quote!
html
When search peaks transform your editorial agenda
At the end of October, the keyword "decorative pumpkin" suddenly jumped by more than 700 % on Google Trends in France, while "recette bûche de Noël" was already beginning its ascent. These sudden accelerations are not anomalies: they are seasonal search trends which, if correctly anticipated, can boost a site's organic traffic and generate unexpected revenue. Journalists in the culinary media don't publish a "Galette des Rois" feature by chance. on 6 January; they know that the demand curve peaks precisely the day before. This type of correlation between public interest and the posting of content online illustrates the need for an editorial calendar calibrated to the actual behaviour of Internet users, and not to vague intuitions.
on 6 January; they know that the demand curve peaks precisely the day before. This type of correlation between public interest and the posting of content online illustrates the need for an editorial calendar calibrated to the actual behaviour of Internet users, and not to vague intuitions.
Cycle analysis: from seasonal inspiration to the granularity of micro-moments
It's no longer enough to just talk about "summer" or "winter". Search engines reveal micro-seasons. In fashion, for example, the expression "women's mid-season coat" peaks in the first two weeks of September, long before temperatures drop. In the consumer technology sector, the cycle is reversed: queries for "best smartphone" peak during Black Friday, but drop off the day after Christmas, replaced by "iPhone configuration tips" or "how to transfer Android data". We are moving from a meteorological logic to a calendar synchronised with commercial calendars (sales, product launches) and decision-making phases ("research online, purchase offline"). Capturing this granularity means dividing up the year into periods sometimes as short as a few days: Valentine's Day, the start of the new school year, tax returns, Prime Day, and so on. Each deserves a specific content angle, adapted wording, and sometimes even a different user intention (informational, transactional or navigational).
The "Evergreen + Seasonal Boost" curve
Some subjects benefit from a permanent evergreen base and a seasonal boost. Take the example of "pollen allergies". This generic keyword is typed in all year round, but in April-May the volume triples, and sub-queries such as "pollen calendar" or "best air purifier against pollen" explode. The strategy is to keep a general guide to allergies (ev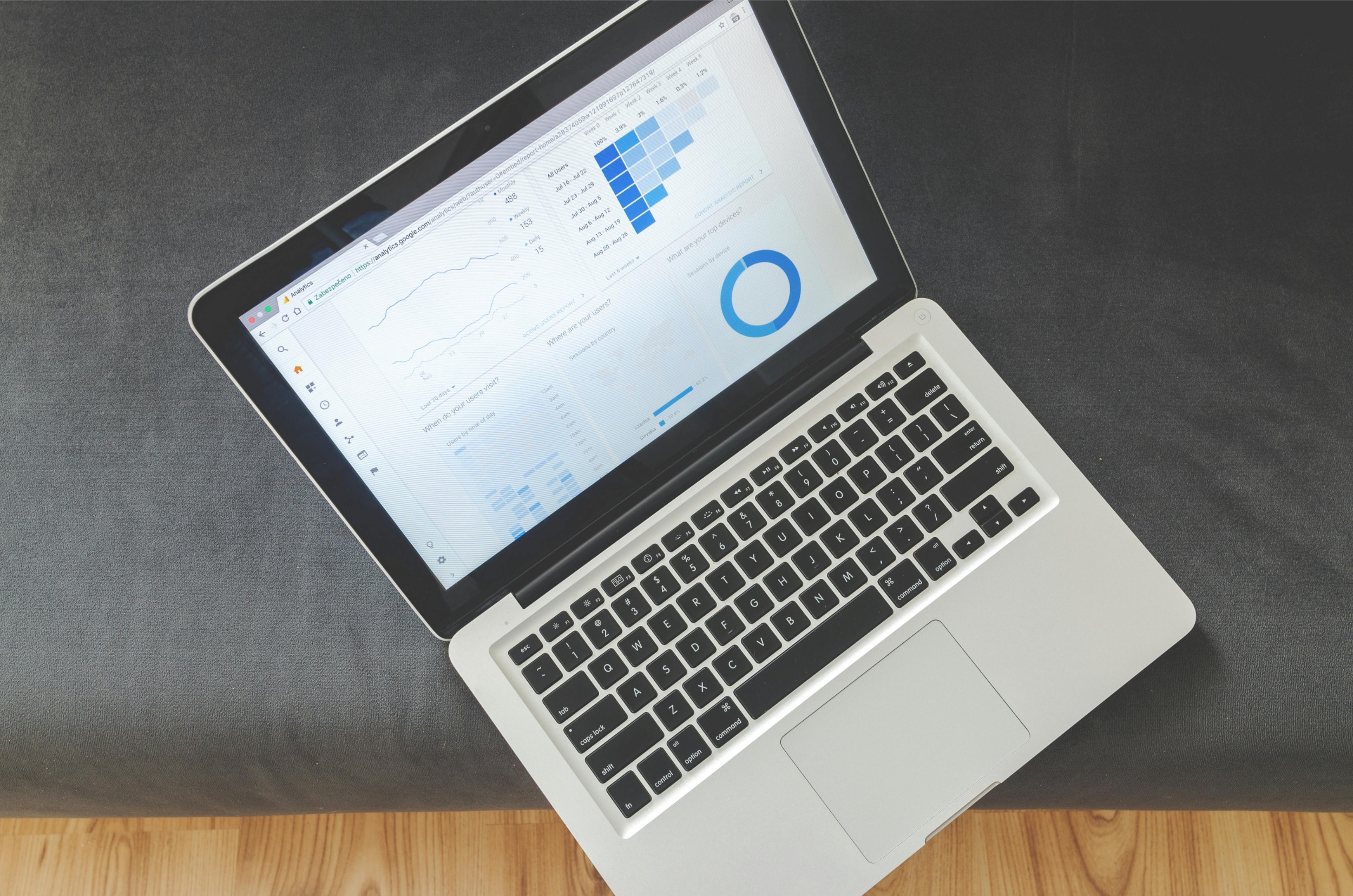 ergreen) and boosting it with satellite articles and intensified internal linking a month before the peak. The result: an increase in clicks across the entire silo, including on pages that were stable for the rest of the year.
ergreen) and boosting it with satellite articles and intensified internal linking a month before the peak. The result: an increase in clicks across the entire silo, including on pages that were stable for the rest of the year.
Case study: the concrete example of BBQ sales during Euro 2016
When France hosted Euro 2016, a household appliance brand specialising in planchas saw an unusual spike in searches for "smokeless electric barbecue". After an autopsy of the search logs, a double effect of summer and sporting events was revealed. The marketing team rushed to create an article entitled "How to build a successful indoor barbecue to watch the match", optimised for the long tail ("build a barbecue in a flat"). The post, published a fortnight before the final, captured 3 times more sessions than the entire blog category over the previous period. This opportunity demonstrates that a seasonal trend can be amplified by one-off events, and that it is possible to hit the ground running if you have an agile workflow.
Methodology: detecting and forecasting search peaks
There is no shortage of tools: Google Trends, SEMrush, Sistrix, Ahrefs, but also APIs from marketplaces (Amazon Best Sellers) and reports from Pinterest or TikTok. The difficulty is no longer in collecting data, but in interpreting it. A sudden spike may be the sign of an ephemeral phenomenon (the release of a Netflix series) rather than a recurring cycle. Hence the importance of extracting at least three years of historical data and smoothing out any anomalies. In Excel or Google Sheets, calculating a 4-week moving average helps to smooth out any major variations linked to the weather, for example. Then, a simple lasso regression model or Prophet (Facebook library) can predict the next rise. Thanks to these forecasts, a YouTube gardening channel is now planning its "pruning your roses" videos from mid-February, while its competitors are still publishing under snowy conditions. Audience gains are in the region of +60 % YOY.
Aligning the editorial calendar: retroplanning and content stacking
Seasonal content is not a one-shot deal. It's called content stacking: a pile of complementary content, published at different times, but designed as a thematic authority engine. To prepare for Dry January, a health magazine published an infographic on alcohol consumption in December (-8 weeks), a guide to buying non-alcoholic drinks (-6 weeks), a video testimonial (-4 weeks) and finally an interactive challenge published on 1 January. This sequence helps 1) to warm up the audience, 2) to move up the SERP before the competition and 3) to create cross-linkages. The conclusion? A CTR multiplied by 2.3 on the expressions "how to stop drinking alcohol for a month" and an explosion in newsletter subscriptions.
The role of updates to existing articles
A content refresh is often more important than a new article. One travel blog has updated its "Where to go in May" and "Where to go in November" pages every year. pages, incorporating post-Covid trends (health restrictions, open borders). The change in publication date from 2021 to 2023 was enough to gain two positions on average. Combined with a change in FAQ tags, the site saw its enhanced extracts displayed in position 0 on "travel in Greece in May" as the summer holidays approached.
SEO optimisations specific to seasonal peaks
Schema.org's Event markup is often underused. However, Google uses it for localised and temporal searches ("Strasbourg Christmas market", "July jazz festival"). For the query "Lyon festival July", records containing rich markup systematically occupy the first event carousels. Similarly, by creating sitemap segments dedicated to seasonal pages, you can tell Google that they deserve to be crawled more quickly, thus avoiding the notorious latency associated with fresh crawl parity. Finally, pay attention to the URL structure. Instead of /noel-2023/, use /noel/ and update the content each year; if necessary, archive the old version in /noel-2022/ to preserve link equity.
SEO/SEA convergence: budgetary arbitrage and cannibalisation
If we are seeing a rise in the popularity of "Mother's Day gifts", should we invest in Ads or rely on organic advertising? A WordStream study shows that in 2022, the average CPC in this niche reached 1.89 $, an increase of 35 % over the previous month. A retailer that had no organic content found itself dependent on paid content, eroding its margin. On the other hand, a boutique selling personalised objects, thanks to an editorial file put online three months earlier, limited its bids while capturing 35 % of additional traffic. This is known as search arbitrage: SEO escalation reduces the need for Ads, freeing up budget for ultra-competitive queries or remarketing.
Keyword bridge strategy
To avoid cannibalisation between SEO and SEA, we identify bridge keywords - those where the organic position stagnates beyond the top 5. SEA then takes over during the peak. Example: "Last-minute ski hire: resort X has never been higher than 6th place organically and doesn't have time to win the battle before the February holidays. It therefore activates an ultra-targeted PPC campaign over the last four weeks, then cuts the flow in March to let organic advertising catch its breath, thus avoiding fuelling off-season CPC inflation unnecessarily.
Seasonal trends and internationalisation: pitfalls and opportunities
A French sunscreen e-commerce company wanted to translate its site into Spanish, convinced that the Mediterranean seasonality was comparable. It failed: in Spain, the peak volume of "crema solar niños" is at the beginning of June, whereas in France the same peak occurs in mid-July (end of school). The one-month time lag resulted in a shortfall of around 12 % on the new shop, due to the lack of content published early enough. Conversely, a B2B player in spare parts for air conditioners took advantage of an opposite window between Australia (summer in December) and Europe. By reusing its article "Signs that you need to recharge your air conditioner with refrigerant", it simply modified the heading and added local references. The result: the same post generated a double flow of business, with the European winter offsetting the Australian low season and vice versa.
Cultural specificities and the lunar calendar
The festivals of Diwali, Chinese New Year and Ramadan do not follow the Gregorian calendar, which complicates planning. A halal recipe site made the mistake of basing its content plan on a fixed April-May approach for Ramadan, even though Ramadan shifts by eleven days each year. The correction consisted in indexing the schedule on the Islamic calendar and automating the dates in the URL via a dynamic slug (/ramadan-2025-recettes). Since then, traffic has increased by 80 % and the brand appears as a featured snippet on "iftar rapide" every spring.
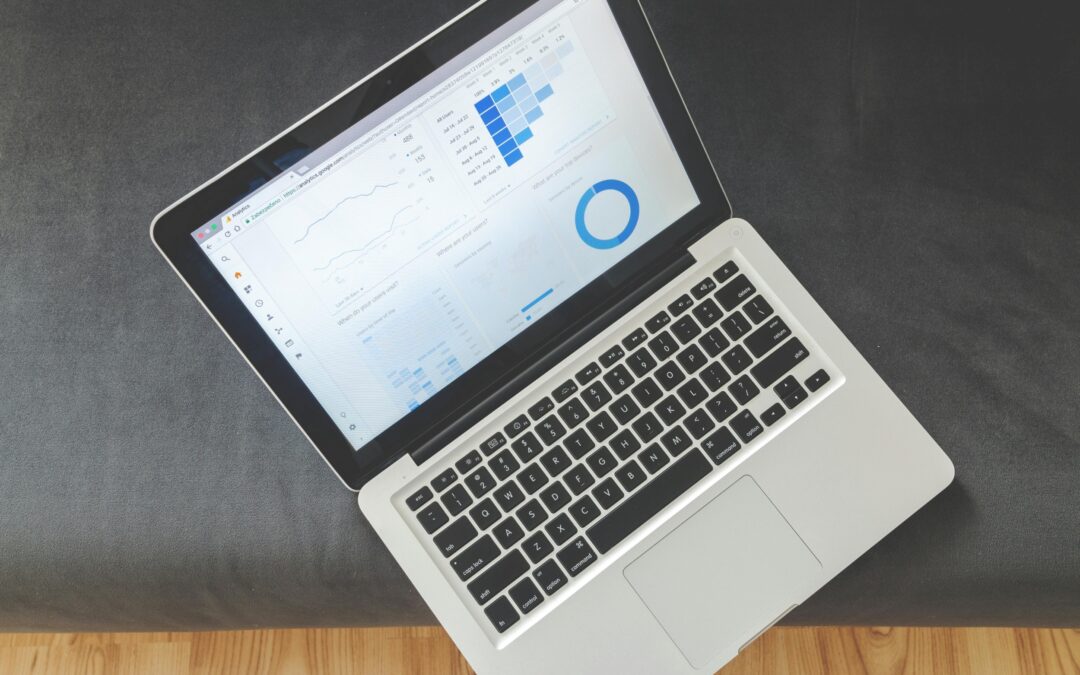
Measuring impact: indicators and attribution
The success of seasonal content can be measured by more than just the volume of visits. We look at the seasonal uplift - the difference between the average off-season traffic and the traffic during the hot period, weighted by the previous year. Monitoring is usually done using Data Studio (Looker Studio) and a regex filter on the URL. A GA4 event tag is added to quantify key interactions (adding to basket, registering). B2B businesses also track time spent on the page and qualified leads. Example: a boiler manufacturer monitors the query "winter water heater failure". The average reading time climbs from 2 minutes in June to 5 minutes in January. More revealing is the rate of use of the quote simulator, which doubles in winter. Multitouch attribution reveals that 40 % of sales come from users who entered via a troubleshooting article, something that the latest e-mail or Ads clicks did not show.
The after-season tail effect
After the peak, well-positioned content continues to attract latent traffic. In the aftermath of Black Friday, many high-tech buying guides are still being consulted for Christmas, with a search volume divided by three but accompanied by a higher conversion rate (+27 %). The phenomenon can be explained: Internet users, reassured by stable prices, are taking action. Negotiating this comet tail means adjusting the message: updated headlines, CTA geared towards express delivery before Christmas and a banner highlighting the extended returns guarantee.
Risk of overheating: out-of-date content syndrome
Publishing on "sales 2023" without updating can lead to a quasi-internal duplicate the following season. Google then downgrades both URLs, unable to determine the correct version. The remedy: systematic archiving or a continuous rewriting mechanism. Unprepared e-tailers often see their old article rise to the top in spite of themselves, displaying obsolete dates. Worse still, users bounce back, sending out a negative signal. Analysis of serps shows that the explicit mention updated on... or guide 2024 in the title improves the CTR by 4 to 6 % during the hours following the online publication. A detail that is sometimes worth more than a backlink.
Beyond text: video, audio and seasonal rich media
TikTok is no exception to seasonal cycles: the #SummerHair trend takes off every May-June; #MondayMotivation takes off again in September (back to school). For a hairdressing medium, recycling an article entitled "6 light cuts for summer" into a vertical video format attracted 1.2 million views, compared with 25,000 readers of the original post. Apple Podcasts reported peak listening figures on good resolutions in mid-January, prompting a sports coach to pre-record an episode with an editorial line almost identical to that of his article. The channels feed off each other; SEO traffic leads to audio subscribers, and vice versa.
Interactive formats and search intent mobile
Web stories (AMP Stories) lend themselves particularly well to party recipes or travel checklists. They appear in Google Discover, whose algorithm is notoriously sensitive to freshness. A decorating website increased its Discover visibility 4-fold with a DIY advent calendar story published at the beginning of November, combined with an animated GIF and a call-to-action to the ribbon shop. The fast, immersive mobile experience is designed for "micro-moment" use - users consult the site while on the move, then save it for later. Desktop sessions on the same queries have also picked up, a sign that the story has acted as a teaser before a longer visit at the end of the day.
Integration of weather and event data in real time
Seasonal traffic models can be enhanced by a weather API: an umbrella shop triggers a push -15 % today as soon as a rainfall rate >70 % is forecast. Similar feeds exist for the world's stock markets (impact on financial content) or for lotteries (record jackpots). The US media even use TV ratings: when the Super Bowl final approaches, the best commercials ever articles are bumped up to the home page. These real-time triggers transform season planning into a hyper-contextual marketing moment.
Automation and AI: predicting intent, generating variants
Artificial intelligence systems such as Prophet for forecasting and GPT-4 for generating headlines can now be used to produce content variations tailored to each phase of the cycle. An HR SaaS, faced with peaks in work-study requests between March and May, has trained a model to automatically adjust its transactional emails: subject line "work-study interview - the 3 points to check before applying in April, then switches to "work-study: 5 offers to be snapped up before the start of the new school year in September" in July-August. Automation does not replace the editor, but it does make the time-to-market more fluid.
Operational checklist for taking advantage of seasonal trends
- Map keywords over 24 months and identify recurring peaks.
- Create an editorial schedule for publication in T-8 weeks (retail) or T-4 weeks (pure media).
- Prepare the dynamic update (titles, years) with a calendar reminder.
- Implement Schema.org Event or Product markup, depending on the context.
- Segment the sitemap to force rapid exploration of fresh pages.
- Monitor CPC and decide on the SEO/SEA ratio according to the organic position achieved at T-2 weeks.
- Plan for cross-channel re-use (story, video, podcast).
- Tag all key interactions to measure seasonal uplift and after-season tail.
- Set up a redirection or automatic update script to avoid out-of-date content.
- Simulate several weather/events scenarios and trigger adaptive content.
Outlook: towards a perma-seasonal content strategy
As the boundaries between seasonality and newsjacking become blurred, brands are adopting a perma-seasonal strategy, combining the logic of recurring cycles with real-time reactivity. Fast fashion is publishing a pre-summer lookbook before the summer has even begun, while fintech is already preparing for taxation in 2025. This long-distance race demands both methodological rigour and tactical flexibility. Those who will capture tomorrow's demand for the next big trend will be those who have understood that the editorial calendar is no longer linear - it beats to the rhythm of countless digital micro-seasons.